12. Social Psychology (Ch 12)
12.1 Attribution Processes
Attribution theory
- dispositional attributions
- internal and trait reasons
- personality or characteristics
situational attributions
- external and state reasons
- based on a person's situation or environement
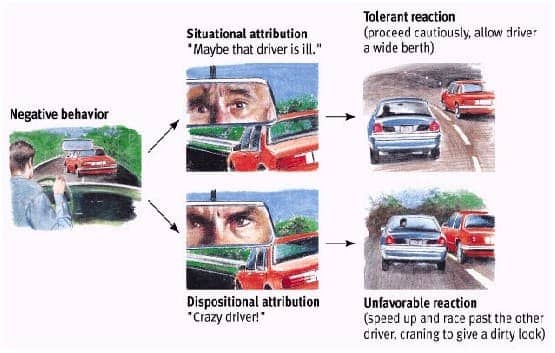
fundamental attribution error
others behavior due to disposition, minimizing role of situation factors

actor-observer bias
viewing others faults as due to dispositional factors, but our faults as situationa

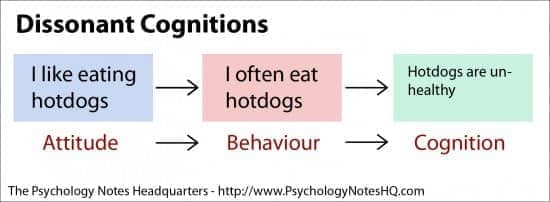
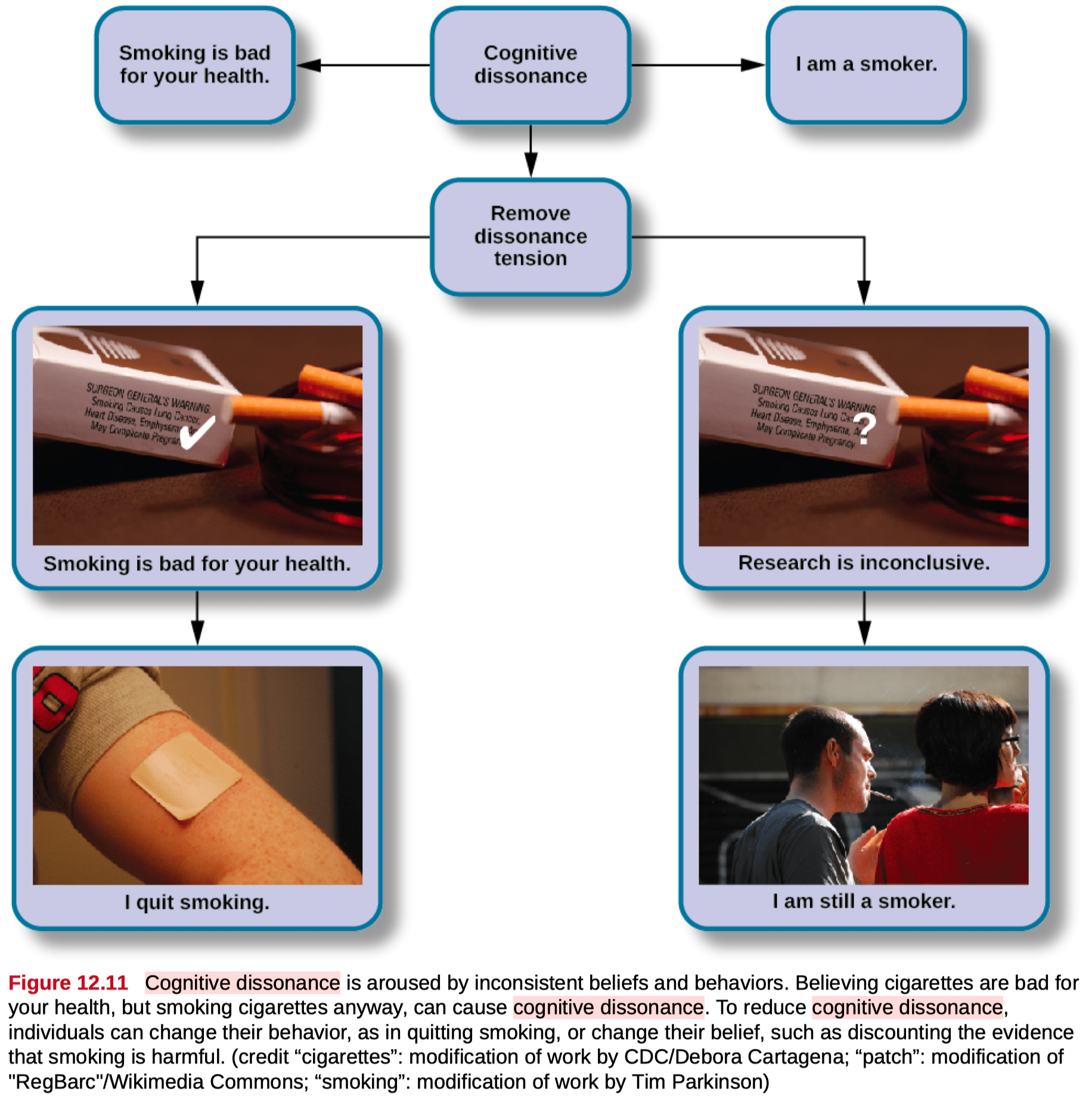
cognitive dissonance theory
psychological discomfort arising from holding two or more inconsistent attitudes, behaviors, or cognitions
- dispositional attributions
12.2 Attitudes and Attitude Change
Attitudes
- evaluation or feelings towards person, idea or object
- positive or negative; favorable or unfavorable
- external and internal influences
- affective, behavioral and cognitive
Attitude Change
cognitive dissonance
- internal influence
- thoughts, feelings and behaviors in conflict
persuasion
- process of changing our attitude toward something based on some form of communication
- foot-in-the-door technique
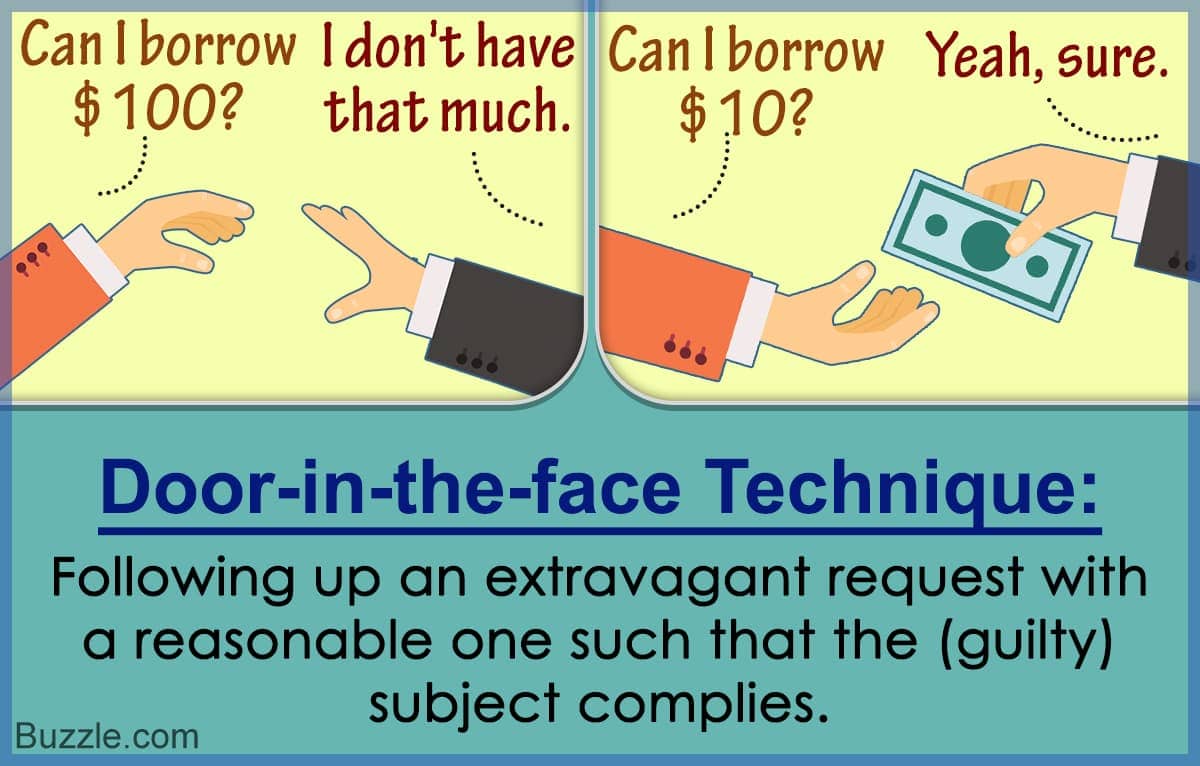
- door-in-the-face technique
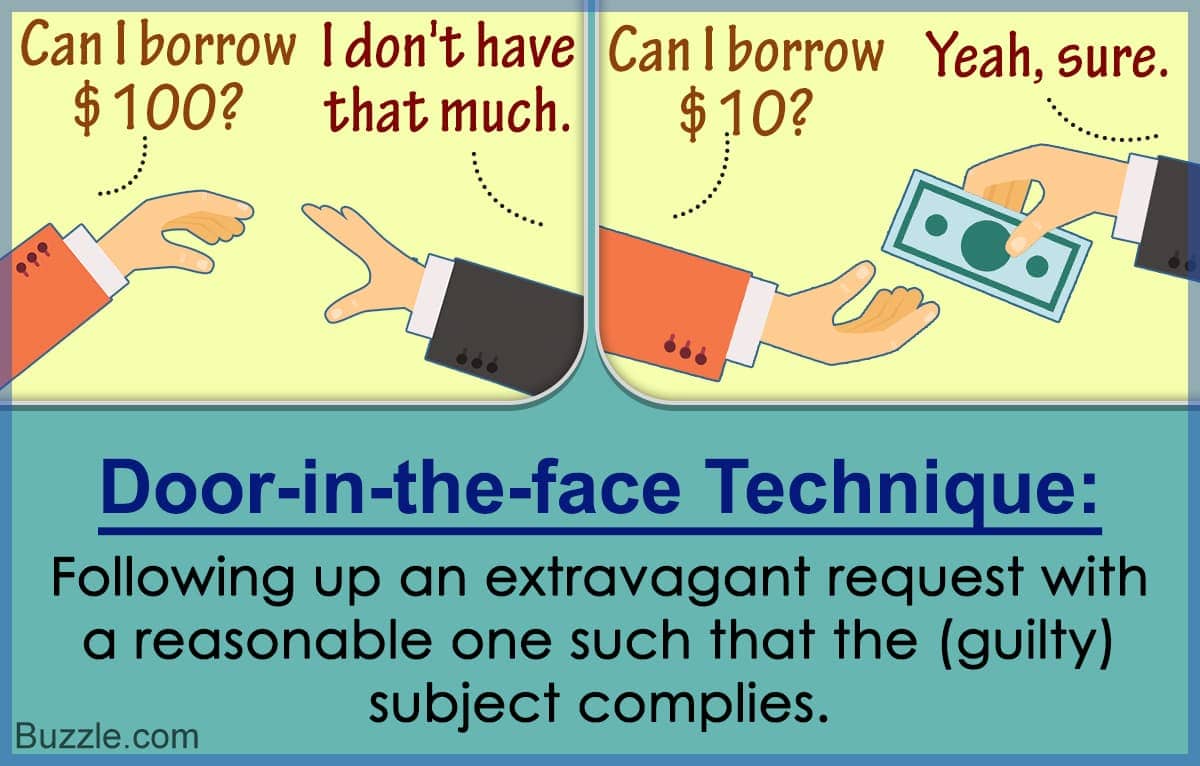
- advertising
12.3 Interpersonal Perception
Awareness of mental acts present within us
Cognitive biases
- Actor-observed bias (10.1)
Halo effect

False consensus
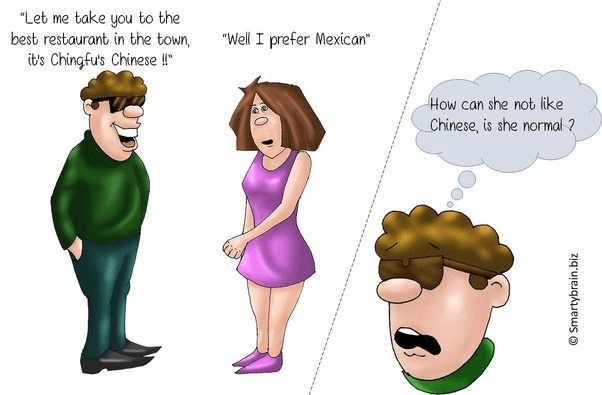
Psychological projection

12.4 Aggression/Antisocial behavior, and Altruism/Prosocial behavior
- Frustration-aggression hypothesis
- it's believed that aggression is always the product of frustration
- frustration, basically always leads to aggression
- Hostile aggression
- intent to cause pain
- Instrumental aggression
- intent to achieve goal

Testosterone
- higher levels, more easily provoked
Antisocial behavior
- lack of remorse
- no care for other people’s feelings
- anger and hostility
- affect expressed through aggressive acts
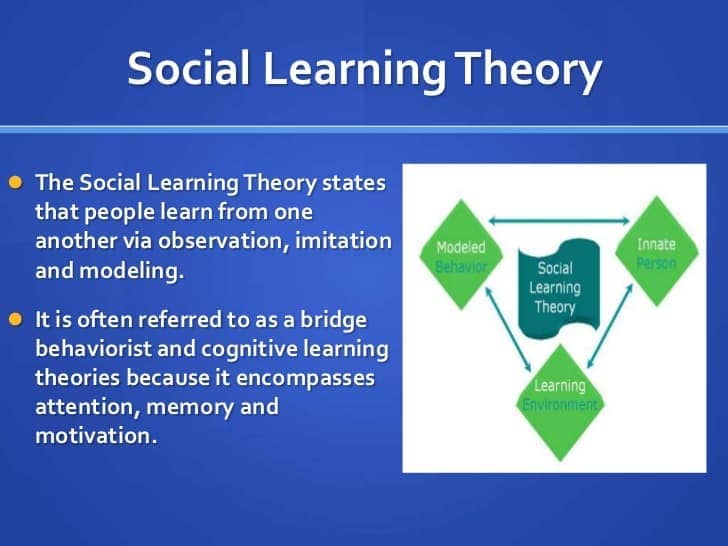
Social learning theory
these elements of acting, behaving, can be learned
Antisocial personality disorder
Prosocial behavior
- Altruism
- behavior aimed at helping others without expectation of reward or recognition
Bystander Effect
- Kitty Genovese

- Altruism
12.5 Conformity, Compliance, Obedience
Conformity
- change in person’s behavior to go along with group
Solomon Asch Experiments
- influence of group majority on individual’s judgment
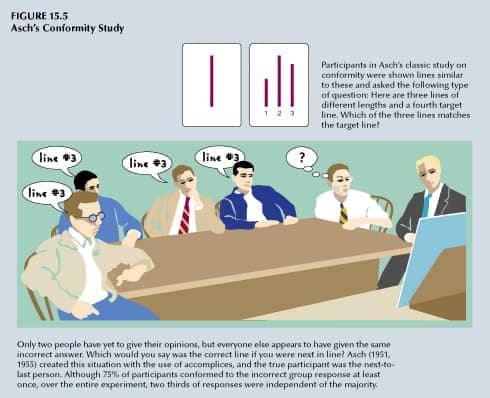
Motivation to Conform
- normative social influence
- conform to the group norm to fit in, to feel good, and to be accepted by the group
informational social influence
- conform because believe the group is competent and has the correct information, particularly when the task or situation is ambiguous
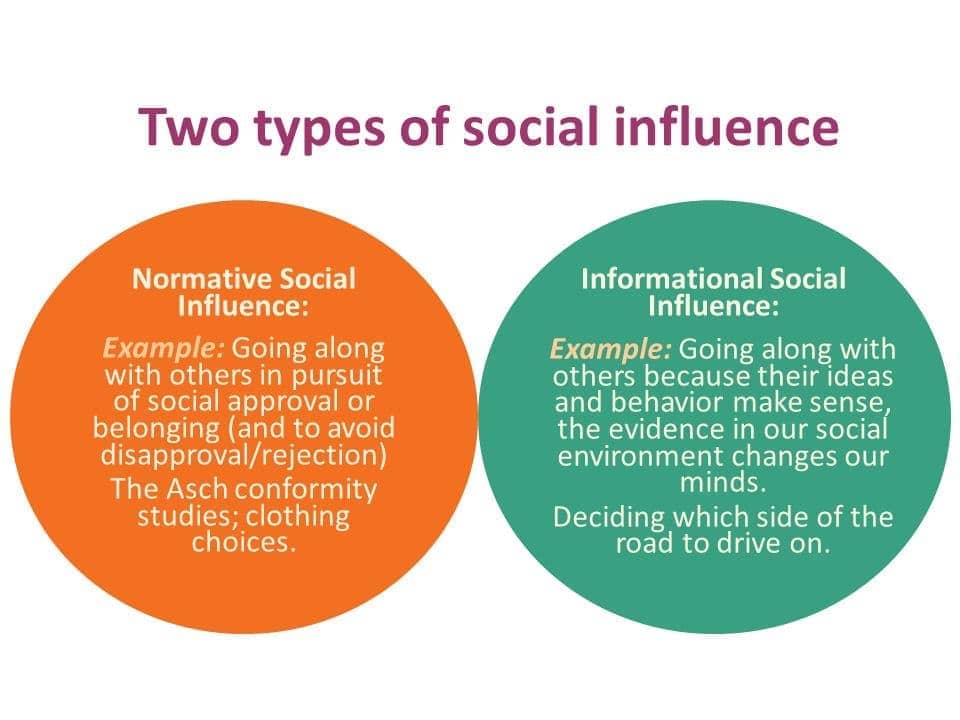
- normative social influence
Compliance
- going along with request or demand
- desire to fit in, be liked and gain information about the group
- groupthink: going along with others to form consensus, even if wrong/disagree
social loafing
- individual performance drops in presence of group (e.g., tug-of-war)

social facilitation
- performing better in presence of others (e.g., sports)

Obedience
- doing what an authority figure tells you to do
- concerned about consequence if they do not comply
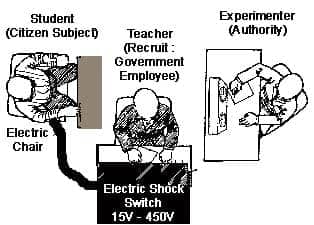
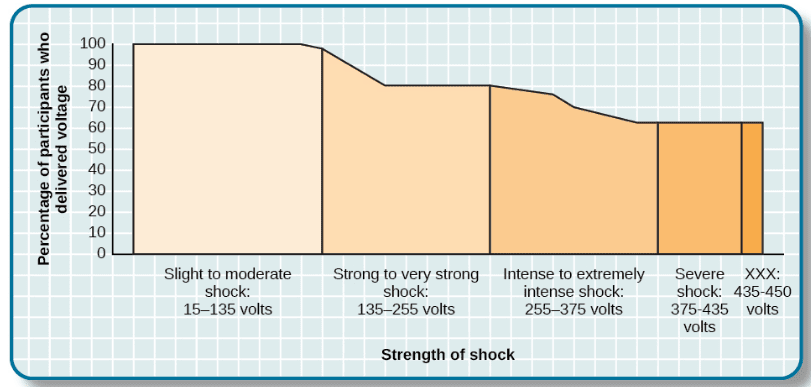
Stanley Milgram Experiments
Quiz
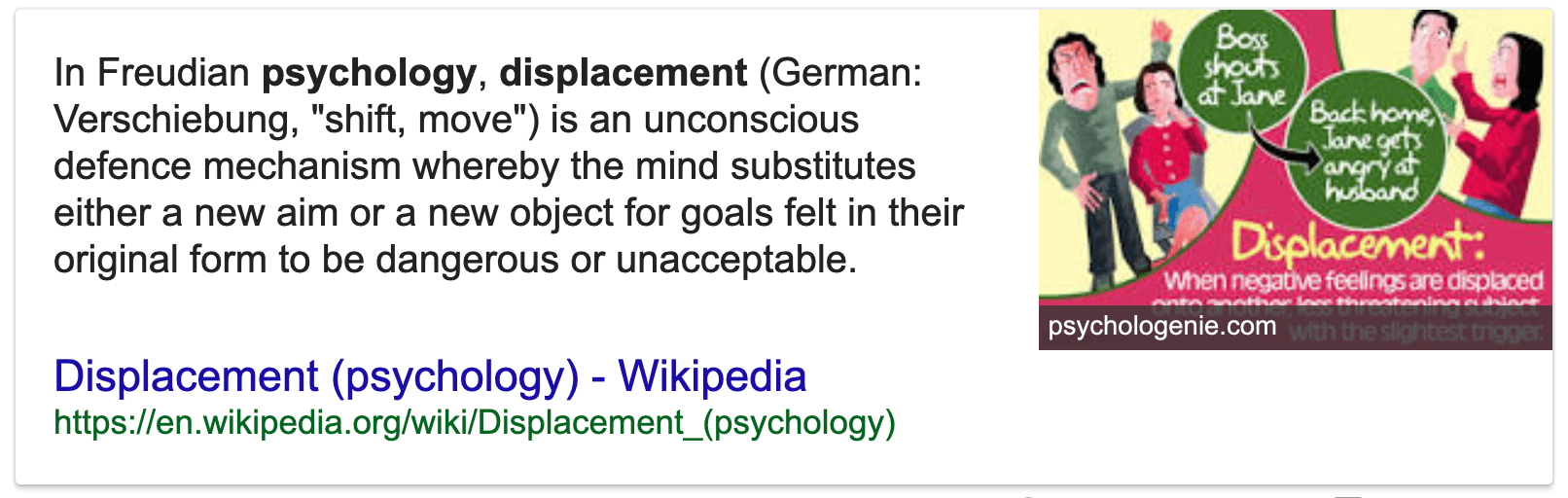
When insulted by a friend, Sally’s first impulse was to strike him. Instead, she yelled loudly and kicked a door several times. This means of reducing aggressive impulses exemplifies which of the following?
- (A) Repression
- (B) Fixation
- (C) Displacement
- (D) Conservation
(E) Sublimation
Tameka regularly sets goals, plans for attaining those goals, and monitors her progress. Her activities are most closely associated with
- (A) high extrinsic motivation
- (B) high achievement motivation
- (C) high extraversion
- (D) low extrinsic motivation
(E) low achievement motivation

Tom fails his math exam. If he explains his failure by using an internal attribution, his reason for failing might be which of the following?
- (A) The teacher was unclear when presenting the material in class.
- (B) Tom’s job did not leave him enough time to study.
- (C) The person sitting next to Tom during the exam was very distracting.
- (D) There was not enough time allotted to complete the exam.
- (E) Tom is not smart or not good at math.
Which of the following terms refers to the strategy of making a small request to gain listeners’ compliance, then making a larger request?
- (A) Door-in-the-face
- (B) Foot-in-the-door
- (C) Social facilitation
- (D) Matching
- (E) Overjustification
Similarity, proximity, and familiarity are important determinants of
- (A) observational learning
- (B) attraction
- (C) sexual orientation
- (D) aggression
- (E) imprinting